Germany
| Federal Republic of Germany Bundesrepublik Deutschland | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Anthem: The third stanza of Das Lied der Deutschen The Song of the Germans | ||||||
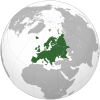
| Location of Germany(dark green) – in Europe(green & dark grey) | ||||||
| Capital (and largest city) | Berlin 52°31′N 13°23′E / 52.517°N 13.383°E | |||||
| Official language(s) | German | |||||
| Demonym | German | |||||
| Government | Federal parliamentary republic | |||||
| - | President | Christian Wulff (CDU) | ||||
| - | Chancellor | Angela Merkel (CDU) | ||||
| - | President of the Bundestag | Norbert Lammert (CDU) | ||||
| - | President of the Bundesrat | Hannelore Kraft (SPD) | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | Holy Roman Empire | 2 February 962 | ||||
| - | Unification | 18 January 1871 | ||||
| - | Federal Republic | 23 May 1949 | ||||
| - | Reunification | 3 October 1990 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 357,021 km (63rd) 137,847 sq mi | ||||
| - | Water (%) | 2.416 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2010 estimate | 81,799,600 (15th) | ||||
| - | Density | 229/km (55th) 593/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2011 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $3.089 trillion (5th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $37,935 (18th) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2011 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $3.628 trillion (4th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $44,555 (19th) | ||||
| Gini (2006) | 27 (low) | |||||
| HDI (2011) | ||||||
| Currency | Euro (€)(2002 – present) (
EUR
) | |||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | DE | |||||
| Internet TLD | .de | |||||
| Calling code | 49 | |||||
| ^ Danish, Low German, Sorbian, Romany and Frisian are officially recognised by the ECRML. | ||||||
| ^ Before 2002: Deutsche Mark (DEM). | ||||||
| ^ Also .eu, shared with European Union member states. | ||||||
Germany ![]() /ˈdʒɜrməni/, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (German: Bundesrepublik Deutschland, pronounced (
/ˈdʒɜrməni/, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (German: Bundesrepublik Deutschland, pronounced (![]() listen)), is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km and has a largely temperate seasonal climate. With 81.8 million inhabitants, it is the most populous member state and the largest economy in the European Union. It is one of the major political powers of the European continent and a technological leader in many fields.
listen)), is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km and has a largely temperate seasonal climate. With 81.8 million inhabitants, it is the most populous member state and the largest economy in the European Union. It is one of the major political powers of the European continent and a technological leader in many fields.
A region named Germania, inhabited by several Germanic peoples, was documented before AD 100. During the Migration Age, the Germanic tribes expanded southward, and established successor kingdoms throughout much of Europe. Beginning in the 10th century, German territories formed a central part of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th century, northern German regions became the centre of the Protestant Reformation while southern and western parts remained dominated by Roman Catholic denominations, with the two factions clashing in the Thirty Years' War. Occupied during the Napoleonic Wars, with the rising of Pan-Germanism inside the German Confederation resulted in the unification of most of the German states into the German Empire in 1871 which was Prussian dominated. After the German Revolution of 1918–1919 and the subsequent military surrender in World War I, the Empire was replaced by the Weimar Republic in 1918, and partitioned in the Versailles Treaty. Amidst the Great Depression, the Third Reich was proclaimed in 1933. The latter period was marked by Fascism and the Second World War. After 1945, Germany was divided by allied occupation, and evolved into two states, East Germany and West Germany. In 1990 Germany was reunified.
Germany was a founding member of the European Community in 1957, which became the EU in 1993. It is part of the Schengen Area and since 1999 a member of the eurozone. Germany is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the G8, the G20, the OECD and the Council of Europe, and took a non-permanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2011–2012 term.
It has the world's fourth largest economy by nominal GDP and the fifth largest by purchasing power parity. It is the second largest exporter and third largest importer of goods. The country has developed a very high standard of living and a comprehensive system of social security. Germany has been the home of many influential scientists and inventors, and is known for its cultural and political history.
Etymology
History
Germanic tribes and Frankish Empire
Holy Roman Empire
German Confederation and Empire
Weimar Republic and Third Reich
East and West Germany
Berlin Republic and the EU
Geography
Climate
Most of Germany has a temperate seasonal climate in which humid westerly winds predominate. The climate is moderated by the North Atlantic Drift, the northern extension of the Gulf Stream. This warmer water affects the areas bordering the North Sea; consequently in the north-west and the north the climate is oceanic. Rainfall occurs year-round, especially in the summer. Winters are mild and summers tend to be cool, though temperatures can exceed 30 °C (86 °F).
The east has a more continental climate; winters can be very cold and summers very warm, and long dry periods are frequent. Central and southern Germany are transition regions which vary from moderately oceanic to continental. In addition to the maritime and continental climates that predominate over most of the country, the Alpine regions in the extreme south and, to a lesser degree, some areas of the Central German Uplands have a mountain climate, characterised by lower temperatures and greater precipitation.
Biodiversity
Politics
Constituent states
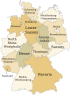
Germany comprises sixteen states that are collectively referred to as Länder. Each state has its own state constitution and is largely autonomous in regard to its internal organisation. Due to differences in size and population the subdivision of these states varies, especially between city states (Stadtstaaten) and states with larger territories (Flächenländer). For regional administrative purposes five states, namely Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Hesse, North Rhine-Westphalia and Saxony, consist of a total of 22 Government Districts (Regierungsbezirke). As of 2009 Germany is divided into 403 districts (Kreise) on municipal level, these consist of 301 rural districts and 102 urban districts.
Foreign relations
Military
Economy
Infrastructure
Science and technology
Demographics
Religion
Languages
Education
Health
Culture
Arts
Literature and philosophy
Media
German cinema dates back to the earliest years of the medium with the work of Max Skladanowsky, which was particularly influential with German expressionists such as Robert Wiene and Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau. Director Fritz Lang's Metropolis (1927) is referred to as the first modern science-fiction film. In 1930 the Austrian-American Josef von Sternberg directed The Blue Angel, the first major German sound film. During the 1970s and 1980s, New German Cinema directors such as Volker Schlöndorff, Werner Herzog, Wim Wenders, and Rainer Werner Fassbinder put West German cinema on the international stage. The annual European Film Awards ceremony is held every other year in Berlin, home of the European Film Academy (EFA); the Berlin Film Festival, held annually since 1951, is one of the world's foremost film festivals.
More recently, films such as Good Bye Lenin! (2003), Gegen die Wand (Head-on) (2004), Der Untergang (Downfall) (2004), and Der Baader Meinhof Komplex (2008) have had international success. The Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film went to the German production Die Blechtrommel (The Tin Drum) in 1979, to Nowhere in Africa in 2002, and to Das Leben der Anderen (The Lives of Others) in 2007. Germany's television market is the largest in Europe, with some 34 million TV households. Around 90% of German households have cable or satellite TV, with a variety of free-to-view public and commercial channels.
Cuisine
Sports
See also
References
- Work cited
Fulbrook, Mary (1991). A Concise History of Germany. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521368360.
External links
- deutschland.de – Official Germany portal (non-profit)
- Official site of German Chancellor
- Deutsche Welle – Germany's international broadcaster
- Germany at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Germany at the Open Directory Project
- Facts about Germany – by the German Federal Foreign Office
- Destatis.de – Federal Statistical Office Germany
 OpenStreetMap has geographic data related to Germany
OpenStreetMap has geographic data related to Germany
 Baden-Württemberg (since 1952)
Baden-Württemberg (since 1952) Bavaria (since 1949)
Bavaria (since 1949) Brandenburg (since 1990)
Brandenburg (since 1990) Hesse (since 1949)
Hesse (since 1949) Lower Saxony (since 1949)
Lower Saxony (since 1949) Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (since 1990)
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (since 1990) North Rhine-Westphalia (since 1949)
North Rhine-Westphalia (since 1949) Rhineland-Palatinate (since 1949)
Rhineland-Palatinate (since 1949) Saarland (since 1957)
Saarland (since 1957) Saxony (since 1990)
Saxony (since 1990) Saxony-Anhalt (since 1990)
Saxony-Anhalt (since 1990) Schleswig-Holstein (since 1949)
Schleswig-Holstein (since 1949) Thuringia (since 1990)
Thuringia (since 1990)
 Baden (south) (1949–1952)
Baden (south) (1949–1952) Württemberg-Baden (1949–1952)
Württemberg-Baden (1949–1952) Württemberg-Hohenzollern (1949–1952)
Württemberg-Hohenzollern (1949–1952)
- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Vatican City
other territories
| Denmark | |
| Finland | |
| United Kingdom |


![Location of Germany (dark green)– in Europe (green & dark grey)– in the European Union (green) — [Legend]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/26/EU-Germany.svg/250px-EU-Germany.svg.png)

