Clioquinol
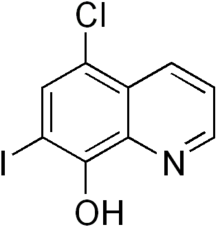 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 5-chloro-7-iodo-quinolin-8-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 130-26-7 |
| ATC code | D08AH30 D09AA10 G01AC02 P01AA02 S02AA05 |
| PubChem | CID 2788 |
| ChemSpider | 2686 |
| UNII | 7BHQ856EJ5 |
| KEGG | D03538 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL497 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C9H5ClINO |
| Mol. mass | 305.499 g/mol |
| SMILES | eMolecules & PubChem |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | ? |
| Legal status | PoM (UK); Rx (US) |
| Routes | topical only |
| | |
Clioquinol (Iodochlorhydroxyquin) is an antifungal drug and antiprotozoal drug. It is neurotoxic in large doses. It is a member of a family of drugs called hydroxyquinolines which inhibit certain enzymes related to DNA replication. The drugs have been found to have activity against both viral and protozoal infections.
Antiprotozoal use
A 1964 report described the use of Clioquinol in both the treatment and prevention of shigella infection and Entamoeba histolytica infection in institutionalized individuals at Sonoma State Hospital in California. The report indicates 4000 individuals were treated over a 4-year period with few side effects.
Several recently reported journal articles describing its use as an antiprotozoal include:
Clioquinol and SMON
Clioquinol's use as an antiprotozoal drug has been restricted or discontinued in some countries due to an event in Japan where over 10,000 people developed SMON (subacute myelo-optic neuropathy) between 1957 and 1970. The drug was used widely in many countries before and after the SMON event without similar reports. As yet, no explanation exists as to why it produced this reaction, and some researchers have questioned whether clioquinol was the causative agent in the disease, noting that the drug had been used for 20 years prior to the epidemic without incident, and that the SMON cases began to reduce in number prior to the discontinuation of the drug. Theories suggested have included improper dosing, the permitted use of the drug for extended periods of time, and dosing which did not consider the smaller average stature of Japanese; however a dose dependant relationship between SMON development and clioquinol use was never found, suggesting the interaction of another compound. Researchers have also suggested the SMON epidemic could have been due to a viral infection with a Inoue-Melnick virus.
Topical use
Clioquinol is used in the drug Vioform, which is a topical antifungal treatment.
Use in neurodegenerative diseases
Research at UCSF indicates that clioquinol appears to block the genetic action of Huntington's disease in mice and in cell culture.
Evidence from phase 2 clinical trials suggested that clioquinol could halt cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease, possibly owing to its ability to act as a chelator for copper and zinc ions. This led to development of analogs including PBT2 as potential therapeutic compounds for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Recent animal studies have shown that clioquinol can reverse the progression of Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases. According to Dr. and colleagues at McGill's Department of Biology, clioquinol acts directly on a protein called Clk-1, often informally called “clock-1,” and might slow down the aging process. They theorize that this may explain the apparent ability of the drug to be effective in the above conditions, but warn against individuals experimenting with this drug.[1]
Continued use and manufacture around the world
References
Retrieved from : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clioquinol